Suspension Systems of Automobiles
Introduction to Suspension System
1.It connects the vehicle body and the wheels, and thus supports the weight of the vehicle.
2.It works together with wheels to absorb vibrations and shocks from the road surface, so as to improve driving comfort and protect the passengers from road socks.
3.It ensures that the wheels are always firmly in contact with the road surface and maintains the inclination of body in order to improve the stability of the vehicle in any possible driving condition including acceleration, braking and cornering.
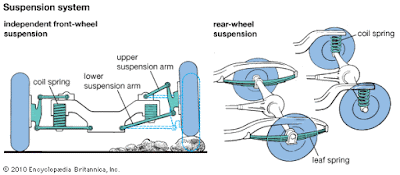
The design and construction of individual suspension components is dependent on the type of suspension system used in the vehicle. The main components of a suspension system are the springs and shock absorbers. The spring support the weight of the vehicle and absorb shocks from the road surface. The shock absorber controls the motion of the springs by damping the spring action. The shock absorbers allow the basic spring movement, but quickly dampen out the bouncing of the wheels up and down after they pass the bumps or holes.
In addition to spring and shock absorbers, the suspension system generally comprises of linkage arms connected to the body and wheel in order to maintain the correct wheel alignment, and stabilizers to prevent the body to roll during cornering and ensure the stability of the vehicle.




Comments
Post a Comment